Kyoto Protocol Day 2025 is on Sunday, February 16, 2025: I have a question about the Kyoto Protocol?
Sunday, February 16, 2025 is Kyoto Protocol Day 2025. Kyoto Protocol - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Kyoto is intended to cut global emissions of greenhouse gases.
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.

What is the easiest way to summarize the Kyoto Protocol?Why are people in the United States arguing about it?The Kyoto Protocol is a protocol to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC or FCCC), an international environmental treaty produced at the United Nations Conference on treaty is intended to achieve "stabilization of greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere at a level that would prevent dangerous anthropogenic interference with the climate system."[1] The Kyoto Protocol establishes legally binding commitments for the reduction of four greenhouse gases (carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, sulphur hexafluoride), and two groups of gases (hydrofluorocarbons and perfluorocarbons) produced by "Annex I" (industrialized) nations, as well as general commitments for all member countries. As of 2008[update], 183 parties have ratified the protocol,[2] which was initially adopted for use on 11 December 1997 in Kyoto, Japan and which entered into force on 16 February 2005. Under Kyoto, industrialized countries agreed to reduce their collective GHG emissions by 5.2% compared to the year 1990. National limitations range from 8% reductions for the European Union and some others to 7% for the United States, 6% for Japan, and 0% for Russia. The treaty permitted GHG emission increases of 8% for Australia and 10% for Iceland. --------------------
The United States (U.S.), although a signatory to the Kyoto Protocol, has neither ratified nor withdrawn from the Protocol. The signature alone is merely symbolic, as the Kyoto Protocol is non-binding on the United States unless ratified. The United States was, as of at least 2005, the largest per capita emitter of carbon dioxide from the burning of fossil fuels.[59] The America's Climate Security Act of 2007, also more commonly referred to in the U.S. as the "Cap and Trade Bill", was proposed for greater U.S. alignment with the Kyoto standards and goals. The current bill is almost 500 pages long, and provides for establishment of a federal bureau of Carbon Trading, Regulation, and Enforcement with mandates which some authorities suggest will amount to the largest tax increase in the history of the United States.[60]
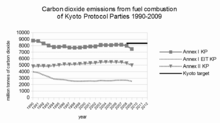
USA refuses the Kyoto protocol?
Bush in 2001 withdrew the USA from the Kyotol protocol.
Vice President Al Gore was a main participant in putting the Kyoto Protocol together in 1997. President Bill Clinton signed the agreement in 1997, but the Republican Senate refused to ratify it, citing potential damage to the US economy required by compliance. The Senate also balked at the agreement because it excluded certain developing countries, including India and China, from having to comply with new emissions standards.
The Kyoto Protocol was negotiated in Kyoto, Japan, in December 1997. It was opened for signature on March 16, 1998, and closed a year later. Under terms of the agreement, the Kyoto Protocol would not take effect until 90 days after it was ratified by at least 55 countries involved in the UNFCCC. Another condition was that ratifying countries had to represent at least 55 percent of the world’s total carbon dioxide emissions for 1990.
The first condition was met on May 23, 2002, when Iceland became the 55th country to ratify the Kyoto Protocol. When Russia ratified the agreement in November 2004, the second condition was satisfied, and the Kyoto Protocol entered into force on February 16, 2005.
As a U.S. presidential candidate, George W. Bush promised to reduce carbon dioxide emissions. Shortly after he took office in 2001, however, President Bush withdrew U.S. support for the Kyoto Protocol and refused to submit it to Congress for ratification.

USA refuses the Kyoto protocol?
Bush in 2001 withdrew the USA from the Kyotol protocol.
Vice President Al Gore was a main participant in putting the Kyoto Protocol together in 1997. President Bill Clinton signed the agreement in 1997, but the Republican Senate refused to ratify it, citing potential damage to the US economy required by compliance. The Senate also balked at the agreement because it excluded certain developing countries, including India and China, from having to comply with new emissions standards.
The Kyoto Protocol was negotiated in Kyoto, Japan, in December 1997. It was opened for signature on March 16, 1998, and closed a year later. Under terms of the agreement, the Kyoto Protocol would not take effect until 90 days after it was ratified by at least 55 countries involved in the UNFCCC. Another condition was that ratifying countries had to represent at least 55 percent of the world’s total carbon dioxide emissions for 1990.
The first condition was met on May 23, 2002, when Iceland became the 55th country to ratify the Kyoto Protocol. When Russia ratified the agreement in November 2004, the second condition was satisfied, and the Kyoto Protocol entered into force on February 16, 2005.
As a U.S. presidential candidate, George W. Bush promised to reduce carbon dioxide emissions. Shortly after he took office in 2001, however, President Bush withdrew U.S. support for the Kyoto Protocol and refused to submit it to Congress for ratification.




















